According to Kaspersky Security Network, between October 2024 and July 2025, over 5,000 users — both individuals and organizations — fell victim to the Efimer trojan. The malware was particularly impactful in Brazil, affecting around 1,500 victims. These attacks also targeted users in India, Spain, Russia, Italy, and Germany.
Kaspersky has discovered a rapidly escalating malicious campaign targeting corporate users with Efimer — a trojan designed to steal and replace cryptocurrency wallet addresses. Initial versions of Efimer appeared in October 2024 and were distributed through compromised WordPress websites. However, in June 2025, the malware began spreading via phishing emails as well. Disguised as a legal firm, the attackers send emails threatening recipients with lawsuits over alleged domain name patent violations to trick them into downloading the malware. This approach allows Efimer to build its own malicious infrastructure and continue spreading to new devices.
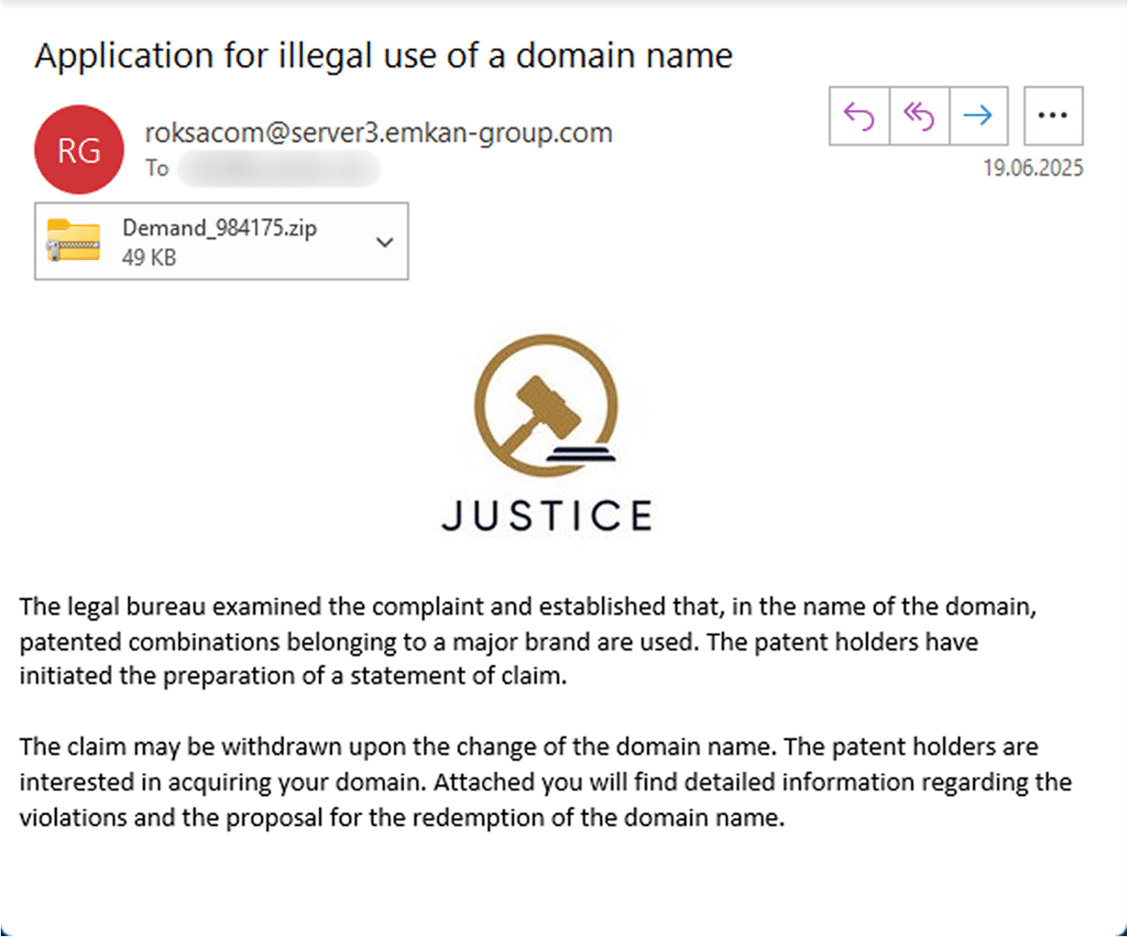
An example of the malicious email
“This Trojan is notable for its dual approach, to spreading — targeting both individual users and corporate environments with different tactics. For private users, attackers use torrent files pretending to be popular movies to lure victims, while in corporate settings, they rely on fraudulent emails containing legal threats. Crucially, in both cases, compromise only occurs if the user actively downloads and executes the malicious file,” explains Artyom Ushkov, threat researcher at Kaspersky.
Find the full report on Securelist.com.
Kaspersky recommends corporate and individual users:
· Refrain from downloading torrent files from unknown or untrusted sources.
· Recipients should carefully verify the legitimacy of email senders and ensure antivirus databases are regularly updated.
· Avoid clicking on links or opening attachments in unsolicited or spam emails to reduce the risk of malware infection.
· Stick to best practice including regular software updates, enforcing strong passwords and two-factor authentication, as well as continuous monitoring for signs of compromise.
· Install a trusted security solution and follow its recommendations. Secure solutions will solve the majority of problems automatically and send alerts.
· For developers and website administrators: implementing robust security measures to protect their infrastructure from unauthorized access and malware propagation is essential.
